What Is Considered An Adequate Sample Size In Statistics
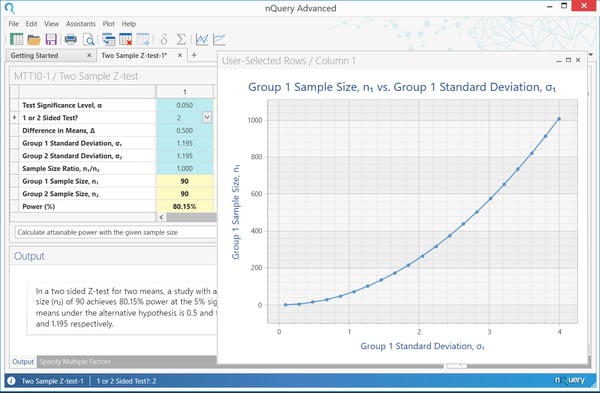
Once steps one to four have been completed, and the appropriate sample size or relevant power has been plant, you lot tin motion onto step 5 which is to explore the uncertainty in your sample size blueprint . The unknown parameters and upshot size that take been defined in steps ii and three are just that - estimates. It is not known what the true value of these parameters should be. If all these parameters were known, in that location would be no demand to run the clinical trial! If the parameters are inaccurate, we risk the possibility of underpowering the written report and not having a big enough sample size to detect the issue size or we may overpower and subject too many people to what may be an ineffective handling. Traditionally, this incertitude would take been explored primarily using sensitivity analysis. A sensitivity analysis is a function of planning a clinical trial that is easily forgotten but is extremely of import for regulatory purposes and publication in peer-reviewed journals. Information technology involves analyzing what issue irresolute the assumptions from parts 2, 3 and 4 would have on the sample size or ability in the item sample size or power calculation. This is important as it helps in understanding the robustness of the sample size guess and dispels the common overconfidence in that initial estimate. Some parameters accept a large degree of uncertainty about them. For example, the intra-cluster correlation is ofttimes very uncertain when based on the literature or a pilot written report, and so it'due south useful to wait at a large range of values for that parameter to see what effect that has on the resulting sample size. Moreover, some analysis parameters will have a disproportionate effect on the last sample size, and therefore seeing what issue even minor changes in those parameters would have on the terminal sample size is very important. When conducting a sensitivity analysis, a choice has to be fabricated over how many scenarios will exist explored and what range of values should exist used. The number of scenarios is normally based on the amount of dubiousness and sensitivity to changes and when these are larger, more scenarios should be explored. The range of values is ordinarily based on a combination of the evidence, the clinical relevance of different values and the distributional characteristics of the parameter. For example, it would exist common to base of operations the overall range on the range of values seen for a parameter seen across a wide range of studies or to base information technology on the hypothetical 95% confidence interval for the parameter based on previous data or a pilot study. For effect size, clinically relevant values volition tend to exist an of import consideration for which range of values to consider. However, it is important to note that at that place is no set rules for which scenarios should be considered for a sensitivity analysis and thus sufficient consideration and consultation should exist used to define the breadth and depth of sensitivity suitable for the sample size determination in your report. A sensitivity analysis for the example to a higher place is shown below. Here, the standard difference in the grouping receiving the new treatment is varied, to assess the effect on the sample size required in that group. The sample size in the control group remains at ninety, and we are always aiming for 90% power. The plot shows that as the standard deviation increases, the sample size required increases dramatically. If the standard deviation is underestimated, a larger sample size is required to attain eighty% power, and thus the trial volition be nether powered. For σ= i.5, 1 = 142, while for σ= two.0, one = 253. This shows the importance of estimating the standard deviation equally accurately as possible in the planning stages, as it has such a large impact on sample size and thus power. Though sensitivity assay provides a nice overview of the effect of varying the issue size or other analysis parameters, it does non present the full picture. It usually just involves assessing a small number of potential culling scenarios, with no gear up official rules for choosing scenarios and how to choice betwixt them. A method often suggested to gainsay this trouble is Bayesian Assurance . Although this method is Bayesian by nature, it is used as a complement to frequentist sample size determination . Assurance, which is sometimes called "Bayesian power" is the unconditional probability of significance, given a prior or prior over some particular fix of parameters in the calculation. These parameters are the same parameters detailed in steps ii and 3 above. In applied terms, assurance is the expectation of the power over all potential values for the prior distribution for the effect size (or other parameter). Rather than expressing the effect size equally a single value, information technology is expressed equally a mean (the value the effect size is virtually probable to be - usually the value used in the traditional power adding) and a standard divergence (expressing your uncertainty about that value). If the power is then averaged out over this whole prior, the upshot is the assurance. This is often framed as the "true probability of success", "Bayesian Power" or "unconditional power" of a trial. In a sensitivity analysis, a number of scenarios are called by the researcher, and assessed individually for power of sample size. This gives a clear indication of the claim of the individual highlighted cases, but no information on other scenarios. With assurance, the average power over all plausible values is determined by assigning a prior to one or more than parameters. This provides a summary statistic for the effect of parameter uncertainty, only less information on specific scenarios. Overall, assurance allows researchers to take a formal approach to accounting for parameter uncertainty in sample size determination and thus create an opportunity to open up a dialog on this result during the sample size decision process. The definition of the prior distribution also allows an opportunity to formally appoint with previous studies and expert stance via approaches meta-analysis or skillful elicitation frameworks such every bit theSheffield Elicitation Framework (SHELF) . O'Hagan et al. (2005) give an case of an assurance calculation for assessing the effect of a new drug in reducing C-reactive poly peptide (CRP) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. " The outcome variable is a patient's reduction in CRP later on four weeks relative to baseline, For the calculation of balls, nosotros suppose that the elicitation of prior information … gives the mean of 0.two and variance of 0.0625. If we assume a normal prior distribution, we can compute assurances with m = 0:2, v = 0.06 … With n = 25, we observe assurance = 0.595 ." This calculation shows that a sample size of 25 per group is needed to achieve power of lxxx%, for the given situation. The assurance calculation can and so exist demonstrated using the "Bayesian Balls for Two Group Examination of Normal Means" table. To view the list ofBayesian Sample Size Proceduresin nQuery, click here. nQuery is the standard for stock-still-term, Bayesian & Adaptive trials Step 5. Explore Parameter Dubiousness
How can nosotros amend upon or supplement the procedure of sample size decision?
What is Bayesian Balls?
How does Bayesian Balls let us explore uncertainty?
What is an example of an Assurance/Bayesian Power calculation for assessing the consequence of a new drug?
and the principal analysis will exist a 1-sided test of superiority at the two.five%
significance level. The (2) population variance … is assumed to be … equal to
0.0625. … the examination is required to have eighty% power to detect a treatment effect of 0.2,
leading to a proposed trial size ofn ane = n 2 = 25 patients … " 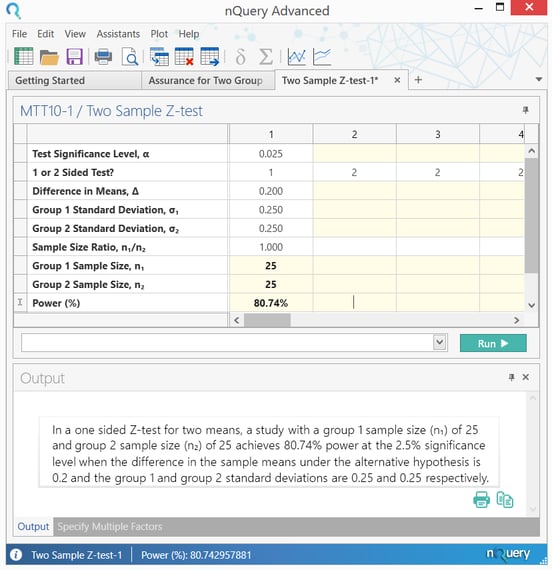
Start your 14 mean solar day gratuitous trial of nQuery
What Is Considered An Adequate Sample Size In Statistics,
Source: https://www.statsols.com/how-to-use-a-sample-size-calculator
Posted by: mcphersonpinge1991.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Considered An Adequate Sample Size In Statistics"
Post a Comment